Alternative cleavage and polyadenylation in health and disease
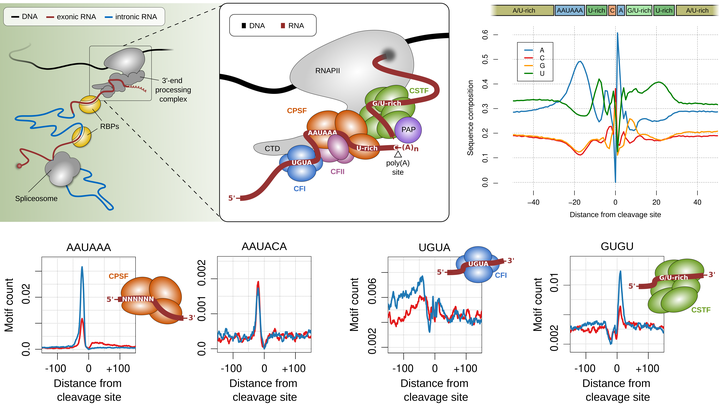
The 3' end of RNA polymerase II transcripts is generated by endonucleolytic cleavage and polyadenylation at 3' end processing sites, also termed poly(A) sites. The processing of 3' end processing sites is mediated by the so called 3' end processing complex, which is a huge machinery that consists out of several subcomplexes (CFI, CPSF, CSTF, CFII) that bind to specific sequence motifs in vicinity to poly(A) sites, the most prominent of which is the so called canonical poly(A) signal (‘AAUAAA’). Most human genes have multiple poly(A) sites and the alternative cleavage and polyadenylation (APA) of these sites gives rise to isoforms that differ in their coding sequence (CDS) and/or their 3' untranslated regions (3' UTRs). The latter harbour cis-regulatory elements that are key regulators of RNA tability, translation and localization.